There are three types of sources: fiber laser, CO2 laser and Nd:YAG laser. The choice of source depends on the type of laser you have chosen (pulsed or continuous).
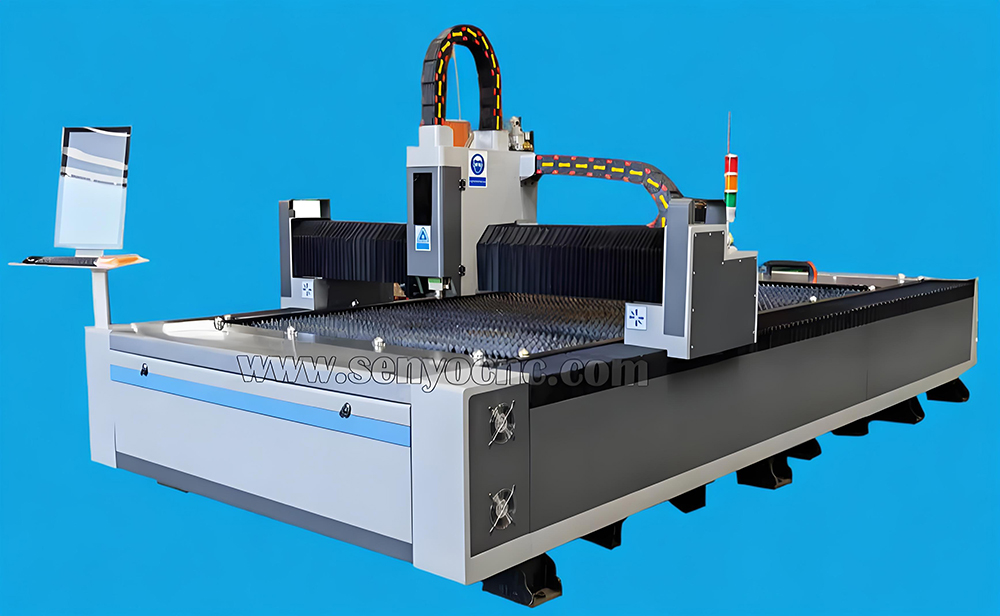
The fiber laser:
This technology is based on sharp and thin beams that allow continuous and penetrative work to be carried out.
Like the CO2 laser, the fiber laser can penetrate thick sheets with great speed and efficiency.
It is easier to integrate into a machine than other lasers both in terms of use and maintenance.
This laser offers an average efficiency of 25%.
The CO2 laser:
This technology uses a gas mixture of carbon dioxide, helium and nitrogen that is electrically-excited and optimized for continuous operation.
Like the fiber laser, the CO2 laser can penetrate thick sheets with great speed and efficiency.
It is more effective at penetrating thick steel parts than the fiber laser so it is more widely used.
It is more flexible and can penetrate thicker and lighter materials than the fiber laser.
This laser offers an average efficiency of 7% for 8,000 W.
The Nd:YAG laser:
It allows effective control of the power, duration and shape of the laser pulses.
It is optimized for pulsed mode.
But it emits pulses of very different wavelengths that do not all reach their target and then dissipate in the form of heat.
This type of laser is less energy efficient (3 to 4% efficiency) than CO2 lasers (7 to 10%) and fiber lasers (25 to 30%).


































































































 manager@senyocnc.com
manager@senyocnc.com
 SENYOCNC
SENYOCNC
 +86 1525 3141 880
+86 1525 3141 880
 +86 1525 3141 880
+86 1525 3141 880
 2061579344
2061579344
