How to Laser Cut Copper and Other Reflective Metals
From: 本站 Date: 03rd September 2021 Author: shengangtong Views: 3611
Laser cutting of mild steel and stainless steel has a long history and has been one of the primary applications for CO2 lasers. However CO2 lasers have not traditionally offered a good solution for cutting highly reflective materials.
Fiber lasers have an emission wavelength of around 1.07 µm, compared to 10.6 µm for traditional CO2 alternatives.
Not only is the 1.07 µm laser light reflected less, and therefore
absorbed more easily, but the shorter wavelength can be focused into a
spot that is around 1/10th of the diameter of a CO2 beam.
This provides a dramatically higher power density, making metal
penetration easier. At such high power density levels, metals such as
copper and brass quickly go through a phase change into molten state,
therefore the laser beam rapidly overcomes the reflectivity barrier of
such metals to initiate an efficient cutting process. Cutting such
metals have shown to be challenging using CO2 lasers or near lasers that have low peak power.
Why is laser cutting brass and copper so challenging?
Their low absorption of infrared laser light makes these metals challenging to cut.
Copper and brass (copper-zinc alloy) are good reflectors (and therefore poor absorbers) of the infrared (IR) laser light, especially in their solid state.
Pure copper reflects > 95% of near-IR radiation (~ 1 µm wavelength) in its solid state.
The reflectivity of copper and other reflective metals decrease when the metal warms up, and drops sharply once the material melts (e.g. down to <70% for copper in its molten state) as seen in figure below. These metals absorb significantly more laser energy in molten state.
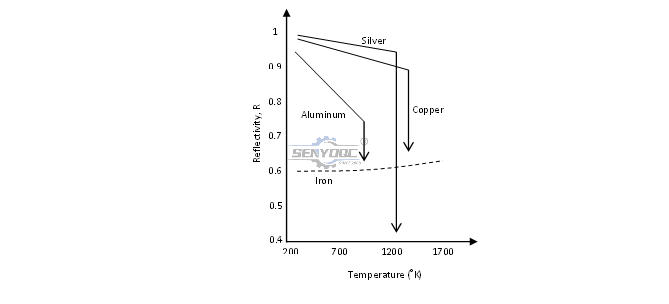
Common problems when laser cutting reflective metals.
When choosing optimized laser, optics, and cutting process, a laser beam
quickly melts the surface of reflective materials to then interact with
the more absorptive molten metal and initiate an efficient, stable
cutting process. Wrong choice of laser/optical setup, or using
non-optimal process parameters can result in excessive dwelling of the
laser with the solid metal, and therefore excessive amount of
back-reflected light. Too much reflection in turn results in the
inefficiency of cutting process and potential damage to optics.
The critical stage in cutting reflective metal is the beginning of the
process, especially the piercing stage when the laser interacts with
solid metal. After the cut is established, laser beam mostly interacts
with the molten material.
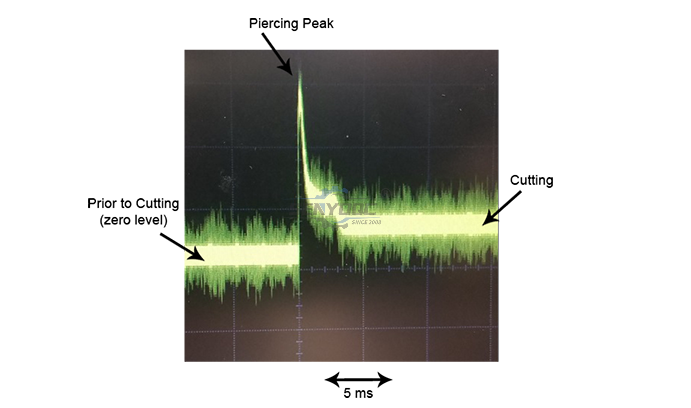
What are the important factors in successful fiber laser cutting of copper and brass?
The following process parameters are relevant for piercing and cutting copper and brass with fiber lasers:
Cut Speed
Back off from the maximum feed rate the process can support by about 10 – 15% to avoid any risk that the cut will extinguish, thereby applying high levels of beam energy to a material in its most reflective state. If in doubt, start at a slower rate than you know the process can support. Allow sufficient dwell time to ensure pierce hole is through before moving the beam to start the cut.
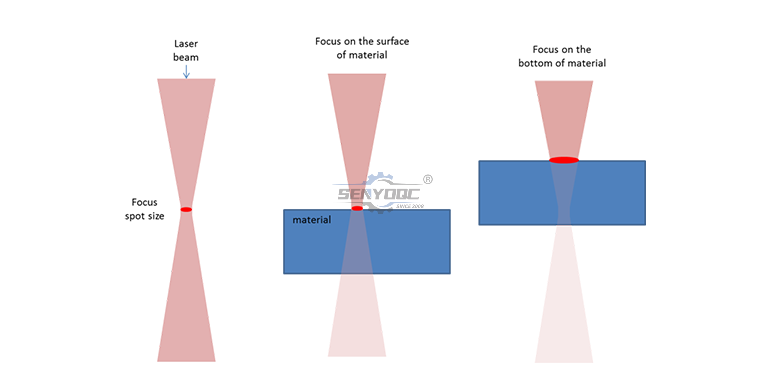
Focus Position
For both piercing and cutting, set the focus position as close to the top surface as the cut quality allows. This minimizes the amount of surface material that interacts with the beam at the beginning of the process, thereby maximizing the power density of the beam, which leads to quicker melting.
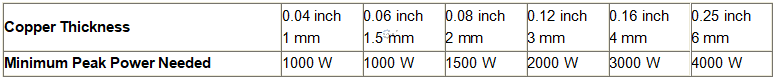
Power Setting
Using the maximum peak power available for the piercing and cutting
reduces the time in which the material is in its most reflective
condition. The chart above can be used as a conservative guide to start
the process development.
Cutting Gas
When piercing and cutting copper, using high-pressure oxygen (100-300 psi depending on the thickness) is typically used as the cutting gas to increase the process reliability. When oxygen is used, the formation of copper oxide on the surface reduces the reflectivity. For brass, nitrogen cutting gas works fine.
• Previous: Precision Cutting Stents with Fiber Lasers
• Next: Fiber Laser Cutting vs. Traditional Sheet Metal Cutting Techniques
Jacob from United States
I am a beginner at CNC, I’ve never used a CNC machine before and with in a day I was carving. An awesome machine for a beginner to learn as hobbyists. I used the manual and the help video. One hour to assemble and test, very friendly and easy to use. It’s a good buy for the money. I would definitely recommend this machine to someone getting into CNCs.
Weinstein from France
I've been using CNC plasma SYP2060-300A and I am very impressed with this unit.
This unit is of higher quality, made in China. Five stars all the way!
2040 from INDIAN
Best 2040 CNC Router Good Price and Quality ! Thank SENYOQC
10w uv laser from American
Best supplier ! I bought 3 machines for laser and router , thank you Aillen ! --Alec
12KW Fiber Cutting - 2000X6000mm -- 이병헌 from Korea
Good machine for metal cut ! Thanks Senyo , Its prefect , I like your business patient kind!
I am a furniture manufacturer, and this machine is very good and fast. thanks Senyoqc Team ! from Bangladesh
Metal ArtWork from Denmark
The plasma cutting machine makes my artistic creation more convenient and precise!! Created more artistic ideas and value! Thank you Aillen team!
Thanks for 3D CNC Router, so much 3D works, just everyday use machine works.that is what makes the magic happen. from
Thanks for 3D CNC Router, so much 3D works, just everyday use machine works.that is what makes the magic happen.
I'm getting a little bit closer to completing more art deco jewelry use fiber laser marking machine.Thank you Senyo from
I'm getting a little bit closer to completing more art deco jewelry use fiber laser marking machine.Thank you Senyo
Thank you Senyo for SYJ1290-150W! from
Retired, ex mainframe systems programmer. Now full-time recreational woodworker majoring in puzzles, pens, boxes, Toys and occasional small furniture. Thank you Senyo for SYJ1290-150W!


































































































 manager@senyocnc.com
manager@senyocnc.com
 SENYOCNC
SENYOCNC
 +86 1525 3141 880
+86 1525 3141 880
 +86 1525 3141 880
+86 1525 3141 880
 2061579344
2061579344
